
AI in Cybersecurity: The Definitive 2026 Guide to Intelligent Threat Detection and Prevention
Last Updated: January 2026
Cybersecurity has changed more in the past five years than it did in the previous twenty.
There was a time when installing antivirus software and configuring a firewall felt sufficient. Today, that approach is dangerously outdated. Attackers are automating their campaigns, using machine learning to discover vulnerabilities, and deploying AI-generated phishing emails that are nearly indistinguishable from legitimate communication.
This is exactly why AI in Cybersecurity has shifted from being an emerging innovation to becoming a core security requirement.
This guide breaks down what’s actually happening in the field, where intelligent systems deliver measurable value, where they fall short, and how organizations are using them responsibly to build long-term resilience.
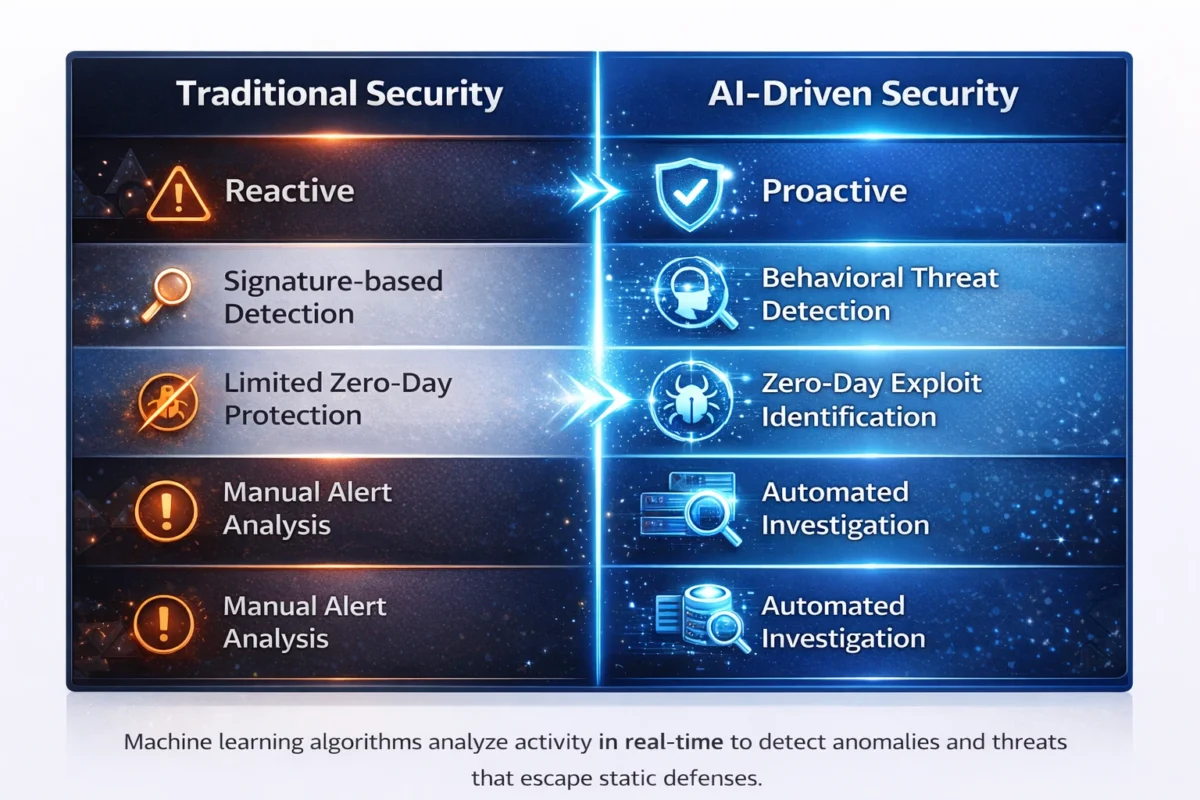
The Modern Threat Landscape: Why Traditional Security Is Struggling
To understand the rise of intelligent defense systems, we need to start with reality.
Security teams today face:
- Exploding cloud infrastructure
- Remote and hybrid workforces
- Increasing API exposure
- Ransomware-as-a-service models
- AI-generated phishing campaigns
- Insider threats with privileged access
Traditional tools rely on signatures and predefined rules. But attackers now modify code constantly to avoid detection. Zero-day vulnerabilities are exploited before patches exist. And phishing messages are personalized at scale.
According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report (2024 edition), organizations using AI-powered security tools reduced breach lifecycle time by over 100 days compared to those without automation.
That reduction translates directly into financial savings, reputation protection, and operational continuity.
This is where AI in Cybersecurity becomes transformative, not because it’s trendy, but because it addresses structural weaknesses in legacy defense systems.
What AI Actually Means in a Security Context
When people hear AI they often think of chatbots or generative tools. In cybersecurity, it’s different.
AI systems in security primarily use:
- Machine learning (ML)
- Behavioral analytics
- Natural language processing (NLP)
- Predictive modeling
- Automated response orchestration
Instead of asking, “Is this file known to be malicious?” modern systems ask:
“Does this behavior look abnormal?”
That shift, from static matching to behavioral analysis, is at the heart of AI in Cybersecurity.
Real-World Case Study: Stopping a Ransomware Attack Before Encryption
In 2023, a multinational logistics firm experienced suspicious internal activity. No malware signature was detected. No traditional alerts were triggered.
However, a behavioral model flagged unusual credential usage patterns. An internal account was accessing systems it had never touched before, at unusual times, across multiple regions.
The system automatically:
- Isolated the affected endpoint
- Revoked compromised credentials
- Blocked lateral movement
The attack chain was disrupted before ransomware encryption began.
There was no public breach. No ransom demand. No operational downtime.
This kind of early detection is a practical demonstration of how AI in Cybersecurity reduces damage windows dramatically.
Core Applications of Intelligent Security Systems
Let’s break down where intelligent automation is delivering the most measurable impact.
1. Behavioral Threat Detection
Modern enterprises generate millions of security events daily. Human analysts cannot manually correlate this volume of data.
AI models establish behavioral baselines for:
- Users
- Devices
- Applications
- Cloud workloads
When activity deviates significantly, the system flags it immediately.
This reduces dependence on known attack signatures.
2. Zero-Day Exploit Identification
Zero-day attacks exploit unknown vulnerabilities. Signature-based systems struggle here.
Machine learning models detect:
- Abnormal memory usage
- Unusual execution flows
- Unexpected privilege escalation
- Suspicious process spawning
Rather than waiting for a threat database update, AI in Cybersecurity identifies irregular patterns that suggest exploitation.
3. Phishing and Social Engineering Defense
Phishing remains one of the most common entry points for breaches.
Modern AI-driven email security platforms analyze:
- Language tone shifts
- Urgency-based manipulation
- Domain spoofing indicators
- Link redirection patterns
With generative AI being used offensively, defensive systems must evolve equally. This “AI vs AI” dynamic is now a central feature of cybersecurity strategy.
4. Cloud Security Monitoring
Cloud misconfigurations are a leading cause of data exposure.
AI systems continuously scan for:
- Excessive user permissions
- Publicly exposed storage buckets
- Suspicious API activity
- Unauthorized access patterns
Manual audits are periodic. AI-based monitoring is continuous.
That shift is one reason AI in Cybersecurity has become foundational in cloud-native environments.
Expert Insight: Where AI Delivers the Most Value
Security professionals consistently identify three high-impact areas:
Threat Correlation at Scale
AI connects seemingly unrelated security events across systems.
Alert Fatigue Reduction
False positives are filtered more effectively.
Faster Incident Response
Automated playbooks reduce response time from hours to seconds.
However, experts also emphasize a key point:
AI enhances analysts. It does not replace them.
Human judgment remains critical in complex investigations and strategic decision-making.
The Dual-Use Problem: Attackers Are Using AI Too
It’s important to acknowledge the other side of the equation.
Cybercriminals now leverage AI for:
- Automated vulnerability scanning
- Deep fake voice scams
- Adaptive malware
- Hyper-personalized phishing campaigns
This escalation is precisely why AI in Cybersecurity is no longer optional.
Defense must evolve at the same speed as offense.
Benefits Organizations Are Experiencing
Organizations adopting intelligent systems report:
- Shorter breach containment times
- Improved detection accuracy
- Reduced operational workload
- Better scalability across hybrid infrastructure
- Improved compliance monitoring
These benefits are measurable, not theoretical.
Implementation Challenges
Despite the advantages, deployment is not frictionless.
Integration Complexity
Legacy systems may not integrate easily with AI platforms.
Data Quality Issues
Poor-quality training data can reduce model accuracy.
Regulatory Considerations
Security data analysis must comply with privacy regulations.
Adversarial Attacks
Attackers may attempt to manipulate AI models through data poisoning.
Understanding these risks is part of responsible implementation of AI in Cybersecurity.
Building EEAT Signals for Trust and Authority
Because cybersecurity impacts financial and personal safety, it falls under Google’s “Your Money Your Life” category. That means credibility matters.
To strengthen EEAT signals:
- Cite reputable industry research (IBM, Gartner, ENISA, NIST).
- Include real-world examples and data.
- Maintain regular content updates.
- Add author expertise (security certifications, IT background).
- Avoid exaggerated claims.
Trust drives rankings in competitive niches.
Future Trends Shaping Intelligent Security
Looking ahead, several developments are gaining traction:
Autonomous Security Operations Centers
Fully automated triage and response pipelines.
AI-Driven Cyber Deception
Intelligent honeypots designed to mislead attackers.
Self-Healing Infrastructure
Systems capable of automatically patching or isolating vulnerabilities.
Quantum-Resistant Security Models
Preparing for future cryptographic disruption.
As these technologies mature, AI in Cybersecurity will become even more deeply integrated into enterprise infrastructure.
Strategic Best Practices for Adoption
If you’re considering implementation, focus on:
- Combining AI tools with skilled analysts.
- Starting with high-impact areas (phishing, endpoint detection).
- Continuously retraining models.
- Conducting adversarial testing.
- Measuring outcomes with defined KPIs.
A phased, measurable approach delivers sustainable results.
Conclusion
Cyber threats are not slowing down.They are becoming automated, scalable, and increasingly sophisticated.
Organizations relying solely on traditional defenses are operating at a disadvantage. The shift toward intelligent systems is not about replacing human expertise, it’s about amplifying it.
AI in Cybersecurity represents a structural evolution in digital defense. It enables earlier detection, faster containment, and more accurate threat prediction.
In 2026, the competitive edge in cybersecurity belongs to organizations that build intelligent, adaptive ecosystems, not reactive ones.
The real question isn’t whether AI will shape cybersecurity’s future. It already is.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is AI in Cybersecurity fully autonomous?
No. While automation handles repetitive tasks and early detection, human oversight remains essential for strategic decisions and complex investigations.
2. Can AI eliminate zero-day threats completely?
No system guarantees complete elimination. However, AI significantly improves detection of abnormal behaviors associated with unknown exploits.
3. How does AI reduce false positives?
By analyzing context and behavioral patterns rather than relying solely on static signatures, AI filters out benign anomalies more effectively.
4. Is AI-driven security expensive to implement?
Initial investment can be significant, but reduced breach costs and operational efficiency often deliver strong long-term ROI.
5. What industries benefit most from AI-driven security?
Finance, healthcare, government, and large enterprises benefit significantly due to high data sensitivity and complex infrastructure.
Call To Action
At Writac, we focus on research-backed insights, real-world case studies, and practical cybersecurity strategies, not hype. Our content is built on industry analysis, credible data sources, and a deep understanding of emerging technologies like AI-driven security.
We prioritize clarity over complexity, helping professionals and businesses make informed decisions with confidence.
